Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Technology is a decentralized digital ledger that is used to record transactions on a secure and transparent platform. It was first introduced in 2008 as the underlying technology behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. However, since then, blockchain has evolved to become a versatile technology that can be used in various industries beyond just finance.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain works by using a network of computers to maintain a shared digital ledger. Each block in the ledger contains a record of transactions, and each block is linked to the previous block using cryptographic hashes. This creates a chain of blocks, hence the name "blockchain".
When a new transaction is added to the blockchain, it is verified and validated by the network of computers, known as nodes. Once the transaction is verified, it is added to a block and added to the chain. The transaction is then considered immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted.
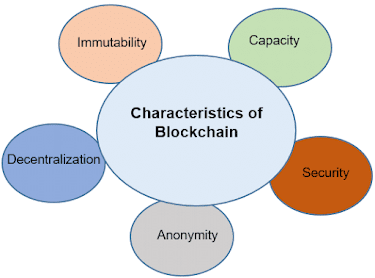
Key Characteristics of Blockchain:
There are several key characteristics that make blockchain unique:
Decentralized: Blockchain is a decentralized technology, meaning that it is not controlled by any central authority. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers, making it transparent and resistant to censorship.
Immutable: Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes it extremely secure and transparent.
Secure: Blockchain uses cryptography to ensure that transactions are secure and tamper-proof. This makes it resistant to fraud and hacking.
Transparent: Because blockchain is a decentralized technology, anyone can view the transactions on the network. This makes it transparent and allows for greater accountability.
Applications of Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain has numerous applications beyond just finance. Some of the industries that have adopted blockchain technology include:
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring greater transparency and accountability.
Healthcare: Blockchain can be used to securely store and share medical records, improving the efficiency and accuracy of healthcare.
Real Estate: Blockchain can be used to facilitate real estate transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
Voting: Blockchain can be used to securely and transparently record votes, ensuring greater accuracy and fairness in elections.
Conclusion:
Blockchain is a powerful technology that has the potential to revolutionize various industries. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it resistant to fraud and hacking, while its transparency and immutability make it a powerful tool for accountability. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more applications and use cases in the future.





0 Comments